| Disease | Injury | Nutrition | Poison |
| Special Topic | Surgery | Symptoms | Test |
|
|
|
|
|
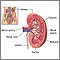
Renal biopsy |
| Definition: |
| A renal biopsy is a means to obtain a sample of the kidney tissue. The sample is then examined in the laboratory. |
| Alternative Names: |
| Kidney biopsy; Biopsy - kidney |
| How the test is performed: |
|
This test is done in the hospital, usually in the radiology suite in ultrasound. You will be expected to follow the instructions given during the test. You will be lying face down on a firm surface. Firm pillows or a rolled towel may be placed beneath the abdominal area to give support. The kidney is located under ultrasound, and then the health care provider will mark the biopsy site (usually the right side). A local anesthetic will be given to numb the skin at the biopsy site. A tiny incision is then made in the skin. You will be asked to take a deep breath, hold it, and remain still as the locating needle (a needle that is used to locate the proper location in the kidney) is inserted through the incision and into the kidney under ultrasound guidance. You will then be asked to take several deep breaths to help verify the position of the needle. The locating needle depth is measured and then removed. The biopsy needle is inserted following the path of the locating needle. Again, the position of the needle will be verified. The sample is taken, and the needle is removed. Pressure is applied to the biopsy site to stop the bleeding, and a bandage is applied. You will remain in the hospital after the test and lie on your back for 12 to 24 hours. |
| How to prepare for the test: |
|
Inform the doctor of any drug allergies you may have, which medications you are taking, if you have bleeding problems, and if you are pregnant. You must sign a consent form. You may be restricted from food or fluid for 8 hours before the test. Infants and children: The physical and psychological preparation you can provide for this or any test or procedure depends on your child's age, interests, previous experiences, and level of trust. For specific information regarding how you can prepare your child, see the following topics as they correspond to your child's age:
|
| How the test will feel: |
|
When the local anesthetic is injected, there will be a prick and a mild stinging. As the biopsy is done, there will be an aching feeling. After the test there may be muscle soreness. You may see bright, red blood in the urine the first 24 hours after the test. If the bleeding lasts longer, inform the health care provider. |
| Why the test is performed: |
|
The test is sometimes used to evaluate a transplanted kidney. It is also used to evaluate an unexplained decreased kidney function, persistent blood in the urine, or protein in the urine. |
| Normal Values: |
| A normal value is when the kidney tissue shows normal structure. |
| What the risks are: |
|
The main risk is bleeding from the kidney which, in 1% of patients, may require a blood transfusion. There is a very minimal chance of infection. There can be bleeding into the muscle, which might cause soreness. |
| Special considerations: |
|
For 2 weeks after the test, avoid strenuous activities and lifting heavy objects. Sometimes a repeat biopsy is needed. |
Reviewed By: Debbie Cohen, M.D., Renal and Electrolyte Division, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 2002 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.