| Disease | Injury | Nutrition | Poison |
| Special Topic | Surgery | Symptoms | Test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
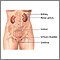
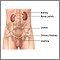
Urinary tract infection (cystitis) |
| Definition: |
| Cystitis is an inflammation of the urinary bladder or urethra. In most cases, cystitis is caused by a bacterial infection and is commonly referred to as a "urinary tract infection." |
| Alternative Names: |
| Bladder infection; Urinary tract infection; UTI |
| Causes, incidence, and risk factors: |
|
Cystitis is usually caused when bacteria enter the urethra and bladder and cause inflammation and infection. It is a very common condition. After infancy, urinary tract infections occur more often in females because their urethra is shorter and closer to the anus. During childhood, about 1% of boys and up to 5% of girls will develop urinary tract infections. In boys the peak age is before the first birthday. Urinary tract infections are much more common among uncircumcised boys. In girls, the peak age for first infections is 3 years, overlapping with the toilet training period. Because cystitis in children can be promoted by abnormalities in the urinary tract, children with cystitis (especially those under age 5) deserve special follow-up to prevent later kidney damage. Older adults are at high risk for developing cystitis, with the incidence in the elderly being as high as 33 out of 100 people. Sexual intercourse can increase the risk of urinary tract infections in women because bacteria can be introduced into the bladder through the urethra. Also, lack of adequate fluids, bowel incontinence, immobility or decreased mobility, indwelling urinary catheters and placement in a nursing home, all place the person at increased risk for developing cystitis.
|
| Symptoms: |
|
| Signs and tests: |
Tests generally include taking a urine sample:
Because many children with cystitis have urinary tracts that predispose them to infections, because these infections are usually preventable, and because the long-term consequences of repeated urinary tract infections in children can be severe, many children with cystitis need special imaging studies to determine why they got their urinary tract infections. These studies usually include both an ultrasound of the kidneys and an x-ray taken during urination (called a voiding cystourethrogram or VCUG). Most experts recommend this evaluation for:
For a girl's first urinary tract infection, recommendations vary on when a complete evaluation is necessary. In young girls, recurrent urinary tract infections may be an indication of a urinary tract abnormality, such as ureterovesical reflux, and should be evaluated by a medical care provider. In boys, a single urinary tract infection indicates the necessity for evaluation, because urinary tract infections in boys are extremely uncommon in the absence of urinary tract abnormalities. |
| Treatment: |
|
Mild cases of acute cystitis may disappear spontaneously without treatment. However, because of the risk of the infection spreading to the kidneys (complicated UTI), treatment is usually recommended. In children, acute cystitis should be treated promptly with antibiotics to protect their developing kidneys. Also, due to the high mortality rate in the elderly population, prompt treatment is recommended. MEDICATIONS: Antibiotics may be used to control the bacterial infection. It is imperative that you finish the entire course of prescribed antibiotics. Commonly used antibiotics include:
Phenazopyridine hydrochloride (pyridium) may be used to reduce the burning and urgency associated with cystitis. In addition, acidifying medications, such a ascorbic acid may be recommended to decrease the concentration of bacteria in the urine. SURGERY: Surgery is generally not indicated in the presence of a urinary tract infection. OTHER THERAPY: Preventive measures may reduce symptoms and prevent recurrence of infection. Keeping the genital area clean and remembering to wipe from front to back may reduce the chance of dragging E. coli bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra. Urinating immediately after sexual intercourse may help eliminate any bacteria that may have been introduced during intercourse. Refraining from urinating for a long period of time may allow bacteria time to multiply, so frequent urination may reduce the risk of cystitis in those who are prone to urinary tract infections. DIET: Increasing the intake of fluids encourages frequent urination that flushes the bacteria from the bladder. Avoid fluids that irritate the bladder, such as alcohol, citrus juices, and caffeine. MONITORING: Follow-up may include urine cultures to ensure that bacteria are no longer present in the bladder. |
| Expectations (prognosis): |
| Cystitis is uncomfortable, but usually responds well to treatment. |
| Complications: |
|
| Calling your health care provider: |
|
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if symptoms indicate cystitis may be present. If you have cystitis, call if symptoms worsen, or new symptoms develop (especially fever, back or flank pain, and vomiting). |
| Prevention: |
| Appropriate hygiene and cleanliness of the genital area may help reduce the chances of introducing bacteria through the urethra. The genitals should be cleaned and wiped from front to back to reduce the chance of dragging E. coli bacteria from the rectal area to the urethra. For those who are prone to urinary tract infections, it may help to drink plenty of fluids, because frequent urination flushes bacteria out the bladder. Urinating immediately after sexual intercourse may help flush out bacteria that may have been introduced with intercourse. |
Reviewed By: Alan Greene, M.D., F.A.A.P., Chief Medical Officer, A.D.A.M.; Clinical Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Stanford University School of Medicine; Attending Physician, Packard Children's Hospital at Stanford (3/3/2002). Previously reviewed by Jeffrey Heit, M.D., Department of Internal Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network (8/24/2001).
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 2002 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.