| Disease | Injury | Nutrition | Poison |
| Special Topic | Surgery | Symptoms | Test |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Crohn's disease |
| Definition: |
|
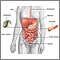
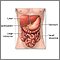
Crohn's disease is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the gastrointestinal tract but most commonly occurs in the ileum (the area where the small and large intestine meet). |
| Alternative Names: |
| Inflammatory bowel disease; Regional enteritis; Ileitis; Granulomatous ileocolitis |
| Causes, incidence, and risk factors: |
|
Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system attacks the body's own cells. In Crohn's disease, these rogue immune cells attack the gastrointestinal system. The cause is unknown, but genetic factors seem to play a role. Inflammation frequently occurs at the end of the small intestine that joins the large intestine, but the condition may affect any area of the digestive tract. As a result of the immune attack, the intestinal wall becomes thick, and deep ulcers may form. The disease may occur at any age, but adolescence and early adulthood are the periods of highest risk. Other risk factors include a family history of Crohn's disease and Jewish ancestry. About 7 out of every 100,000 people will develop Crohn's disease. |
| Symptoms: |
Additional symptoms that may be associated with this disease include the following: |
| Signs and tests: |
|
An abdominal examination may reveal a mass (aggregation of cells) or tenderness.
A stool culture may be done to rule out other possible causes of the symptoms. This disease may also alter the results of the following tests: |
| Treatment: |
|
Your health care provider may prescribe medications such as 5-aminosalicylate to control the inflammatory process. If this is not effective or if the case is severe, treatment may require corticosteroids and immunomodulators such as azathioprine or 6-mercaptopurine. If you have abscesses and/or fistulas, your health care provider may prescribe antibiotics. Infliximab (an antibody to an immune chemical called TNF-alpha, which promotes inflammation) is effective for patients with fistulous disease and those with moderate to severe disease. If medical therapy is not effective, you may need surgery to remove a diseased or strictured segment of the bowel or to drain an abscess. However, unlike ulcerative colitis, surgical removal of a diseased portion of the intestine does not cure the condition. Changes in diet may improve symptoms (consult your health care provider or dietician). An adequate intake of calories, vitamins, and protein is important. Foods that worsen diarrhea should be avoided -- specific food problems may vary from person to person. People who have blockage of the intestines may need to avoid raw fruits and vegetables. Some people have difficulty digesting lactose (milk sugar) and need to avoid milk products. |
| Expectations (prognosis): |
|
This is a chronic disease characterized by periods of improvement followed by deterioration and increased symptoms. There is an increased risk of small bowel or colorectal carcinoma associated with this condition. |
| Complications: |
|
| Calling your health care provider: |
|
Call for an appointment with your health care provider if symptoms worsen or do not improve with treatment or if new symptoms develop. |
Reviewed By: Jenifer K. Lehrer, M.D., Department of Gastroenterology, Graduate Hospital, Philadelphia, PA. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network.
The information provided herein should not be used during any medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. A licensed physician should be consulted for diagnosis and treatment of any and all medical conditions. Call 911 for all medical emergencies. Links to other sites are provided for information only -- they do not constitute endorsements of those other sites. Copyright 2002 A.D.A.M., Inc. Any duplication or distribution of the information contained herein is strictly prohibited.